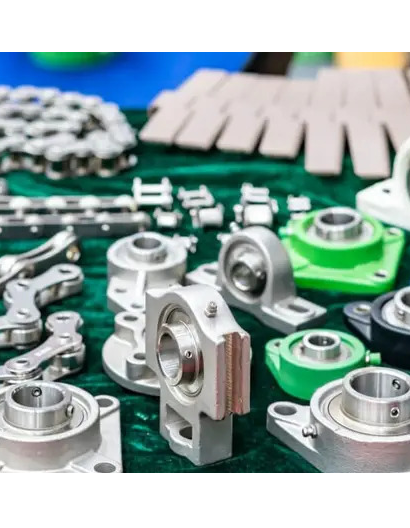

Bearings for conveyor & automation Bearings are used in conveyor rollers to support the weight of conveyed materials and provide low-friction rotation, ensuring smooth movement along the conveyor path.
Self-Aligning Turning Roll is a key piece of equipment for both heavy and light fabrication shops. It is used to rotate or position cylindrical works for circumferential welding (TIG / MIG / SAW) or complex assembly.
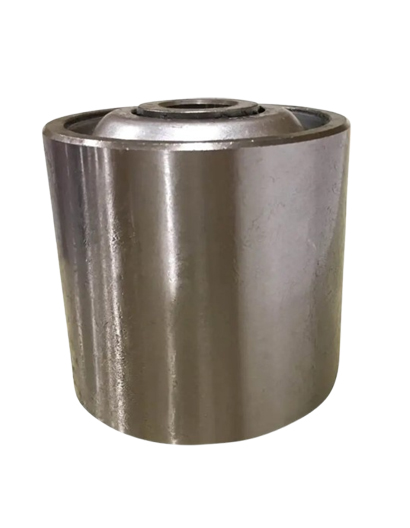
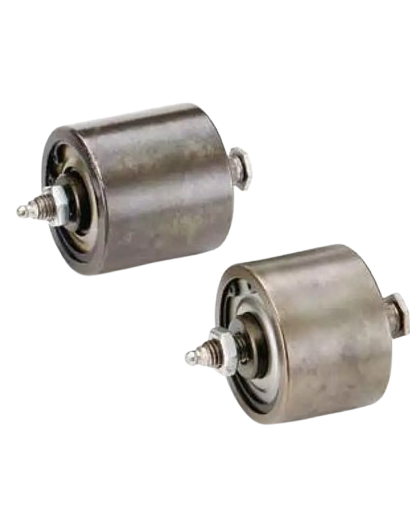


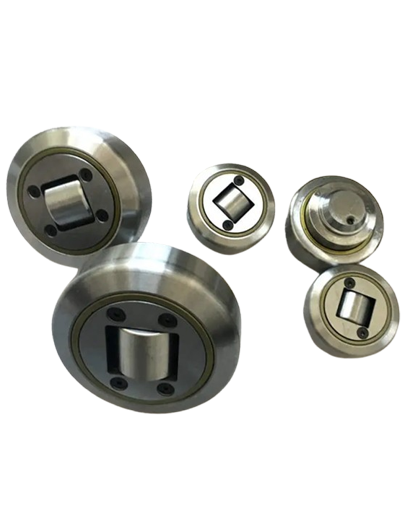
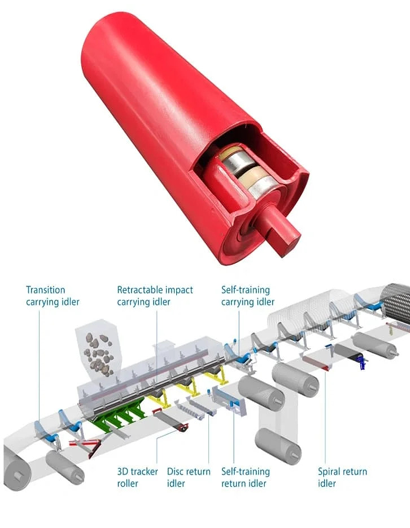
Idlers are cylindrical rollers that run along and under a conveyor belt to support the belt and its cargo. They are the most common conveyor component, and there are many different types with different functions. Idlers’ main purpose is to support the belt and cargo while minimizing the power needed to move the materials. They also help the belt move smoothly and continuously, and prevent it from stretching, sagging, and failing.
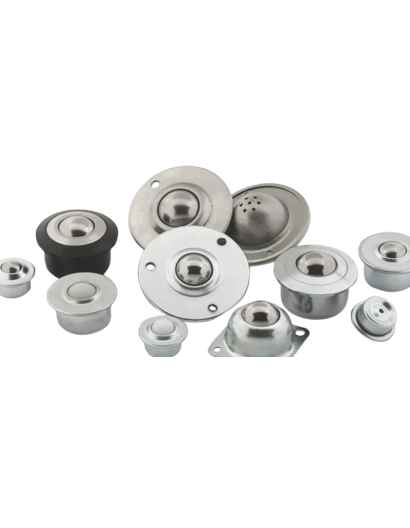
Ball transfer units are critical components in conveyor technology, allowing for flexible and low-friction transportation of goods on conveyor systems. They are made up of a running ball embedded in a housing with additional balls that allows for 360-degree movement.

Guide wheels are used in machinery and gates to aid linear motion. These wheels are generally subjected to frequent yet brief loads. Running wheels, on the other hand, are intended to withstand continuous and steady loads. They are widely utilized in conveyor systems.
shims, spacers and thrust washers from material thicknesses ranging from 0.10 mm – 5 mm. ASPC provides volumes between 100 to 100,000,000 pieces for a number of applications including automotive and off-road transmission & drivetrain as well as farm implement, appliance and others.A cam follower bearing is a roller or needle bearing that is intended to follow cams or tracks. These bearings are employed in linear motion systems such as transfer lines, conveyors, and industrial machines.
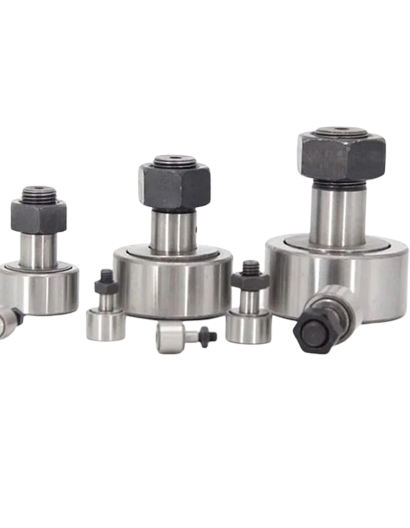

They can support both radial and axial loads. They are especially useful for applications where other forms of locating bearing arrangements take up too much space, where axial loads are too heavy, speeds are too high, or the lubrication is insufficient for setups with basic thrust washers.
